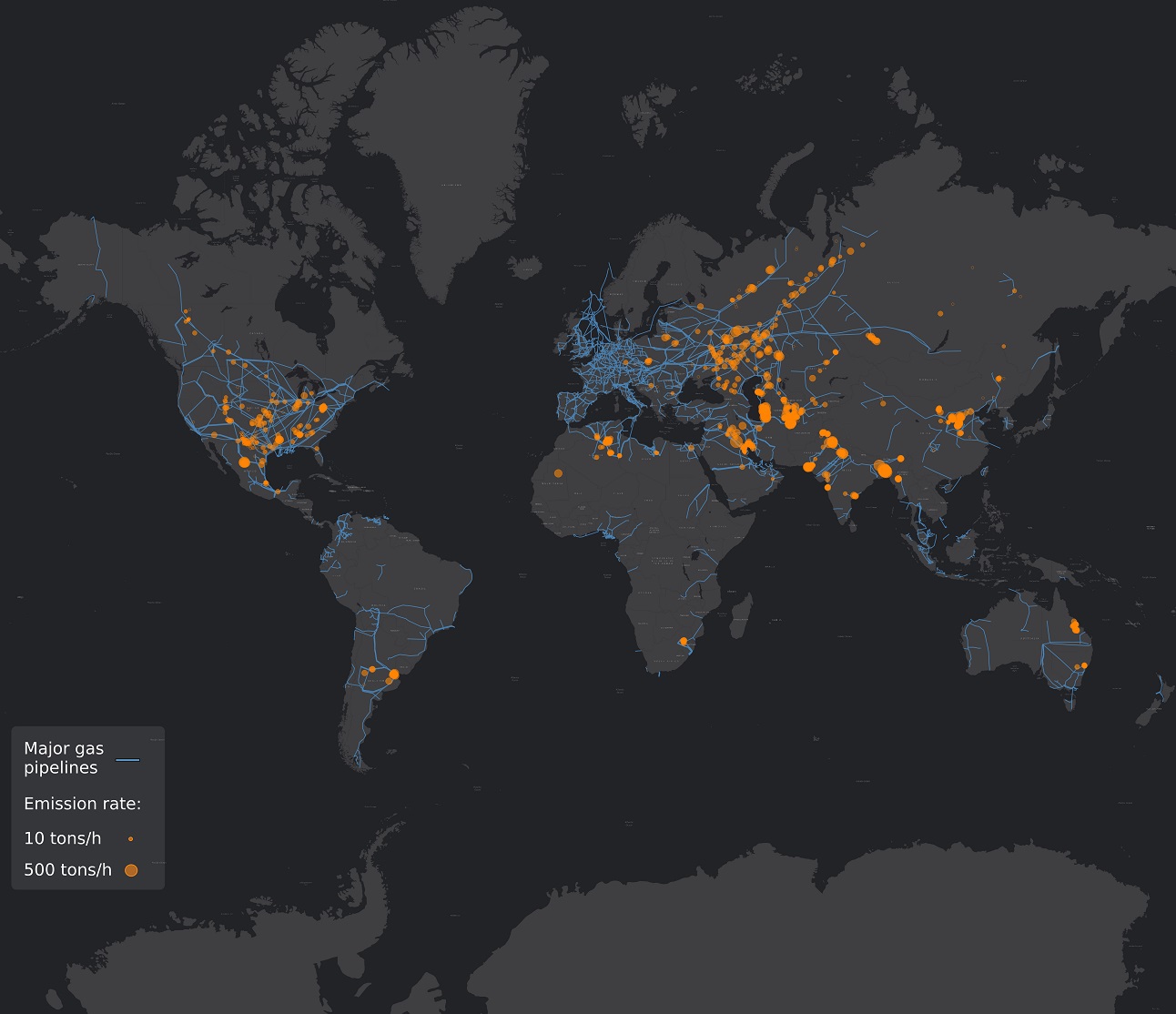
An international team of scientists has mapped the global footprint of giant methane leaks from oil and gas operations for the first time, thanks to high-resolution data delivered by Copernicus Sentinel-5P. This analysis of the potent planet-warming gas – which revealed thousands of large plumes that spilled out from major oil and gas pipelines – could have a key role in the revitalised international drive to tackle the climate crisis.
Methane is less abundant in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide, but it is a more powerful heat-trapping gas. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, it is estimated to have contributed to 30-50% of current global temperature increases. As a result, scientists believe that addressing methane leaks from human activities could be key in efforts to address climate change – and at COP26 last year over 100 countries set out a bold new commitment to cut these emissions.
Copernicus Sentinel-5P reveals oil and gas ultra-emitters
Sentinel-5P – the first mission of the European Union’s Copernicus Programme dedicated to monitoring air pollution – is transforming scientist’s understanding of emissions in the atmosphere. The satellite’s TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) detects the unique fingerprints of gases across different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, delivering daily high-resolution global information on emissions.
From 2019 to 2020, the instrument revealed numerous individual incidences of unintended and deliberate giant methane leaks around the planet. As part of the research, scientists used this set of data to build a comprehensive global picture of emissions hotspots [1]. A method developed by ESA-backed data analytics firm Kayrros was used to generate daily information on methane plumes. An automated detection algorithm – which takes into account changes to meteorological conditions – was applied to the Copernicus data to identify large methane plumes, and further advanced analysis was used to determine leak duration. The resultant emissions were quantified using a mathematical modelling approach.
TROPOMI measurements over the sea have only been available since November 2021, so offshore areas were not included in the analysis. High-altitude regions and areas with cloud cover were also excluded due to high uncertainties in the data. The research suggests that a relatively small number of super-emitter sites are responsible for a disproportionally large share of emissions.
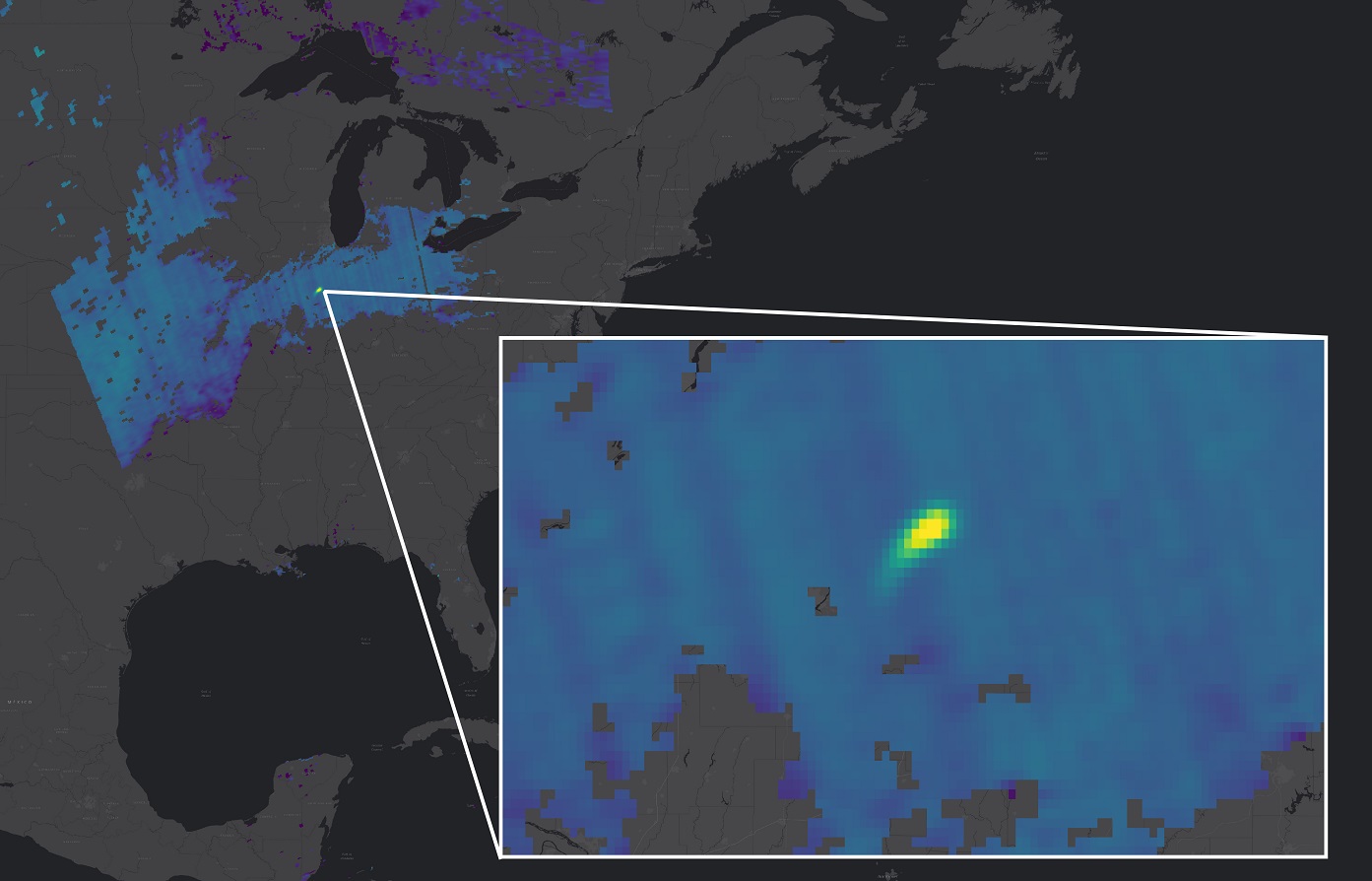
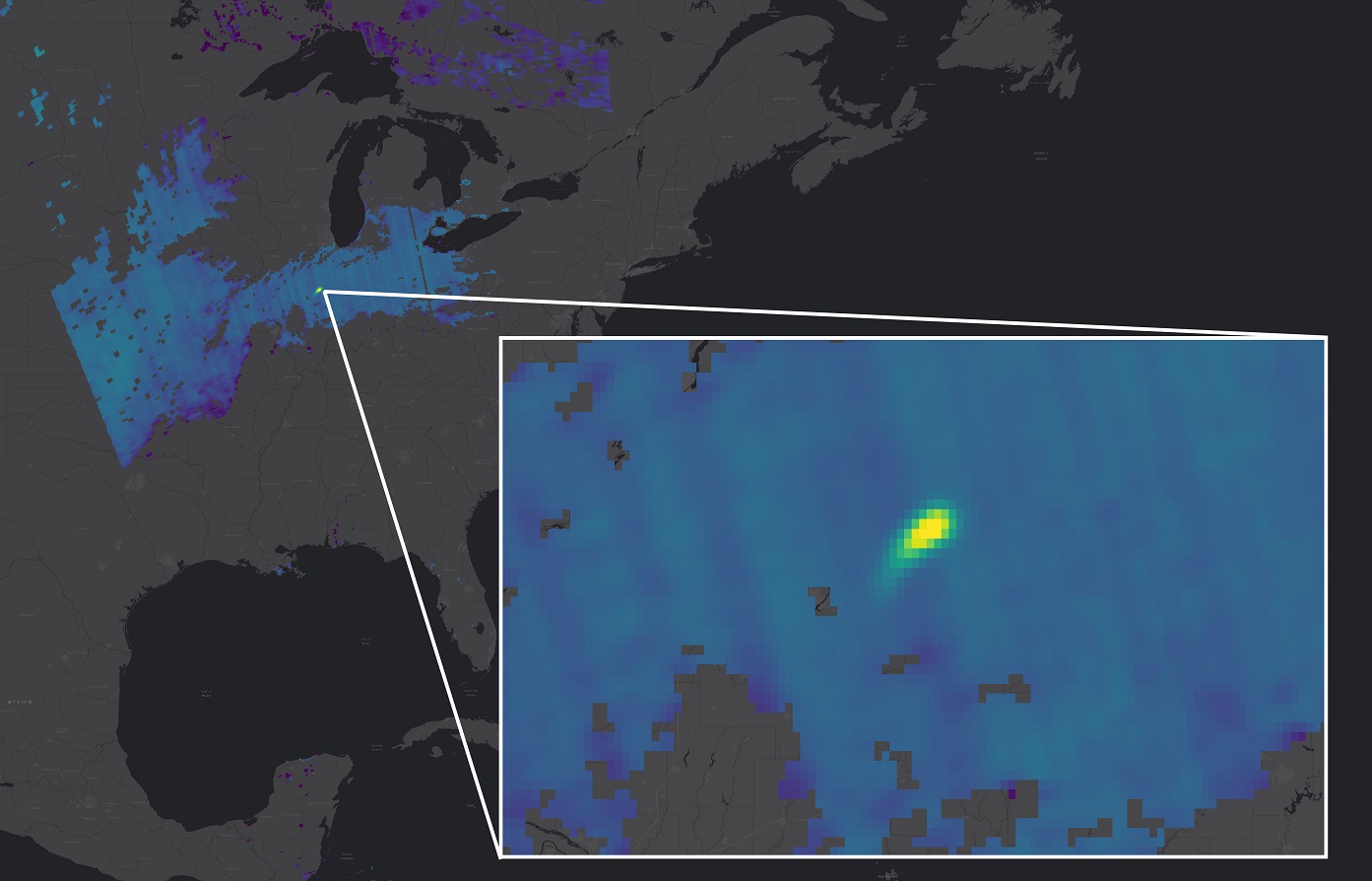
Copernicus Sentinel-5P detects a methane plume over the US
Some 1800 leaks were revealed during the two-year period; about two-thirds of these emissions were associated with oil and gas production or distribution networks. Super-emitter sites were found to release some 8 million tonnes of methane per year. This has an equivalent planet-warming potential of about 250 million tonnes of carbon dioxide [2] in the first 100 years after its release into the atmosphere, or 680 million tonnes of carbon dioxide over the first 20 years. Eliminating these emissions would prevent a global temperature increase of between 0.005°C and 0.002°C, the research suggests [1].
Through analysing the potential costs of mitigation strategies, the researchers reported that leaks at super-emitter sites can be cut relatively cheaply, if industry invests in prevention measures. These findings could help to inform future economical strategies to reduce the impact of oil and gas operations on climate change, as well as helping the international community keep to the Global Methane Pledge, which is a global initiative that aims to reduce methane emissions by 30% by 2030.
In future analyses, Copernicus Sentinel-5P data will be used in synergy with Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery to improve understanding of the sources of large methane leaks. This approach is also expected to enhance resolutions of methane emission maps and improve the sensitivity threshold. Thomas Lauvaux, French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) Research Scientist at the Laboratory for Sciences of Climate and Environment (LSCE), says, “To our knowledge, this is the first worldwide study to estimate the amount of methane released into the atmosphere by maintenance operations and accidental releases. “National greenhouse gas emissions relies primarily on self-reporting, while atmospheric data offers a more rigorous approach to emissions accounting, more independent and more transparent.”
Alexandre d’Aspremont, Chief Scientist at Kayrros, states, “Identifying methane ultra-emitters is the first step to removing them, which is in turn the fastest way to bend the climate curve. It is essential for tackling the climate crisis and informing commercial and industrial decisions. “Our artificial intelligence driven data analysis and algorithms help Copernicus deliver comprehensive monitoring of methane hotspots and detect emission events that escape aerial surveys and local monitoring stations. We look forward to supplying this analysis into the future and help countries and companies realize COP26 Net Zero pledges."
Claus Zehner, ESA’s Mission Manager for Copernicus Sentinel-5P, adds, “This exciting research demonstrates the strong contributions of Copernicus Sentinel-5P to greenhouse gas and climate mitigation efforts both within Europe and globally. “Sentinel-5P satellite is a powerful space-based tool to support the monitoring of the implementation of the European Union’s Methane Strategy as part of the European Green Deal.”
About the Copernicus Sentinels
The Copernicus Sentinels are a fleet of dedicated EU-owned satellites, designed to deliver the wealth of data and imagery that are central to the European Union's Copernicus environmental programme.
The European Commission leads and coordinates this programme, to improve the management of the environment, safeguarding lives every day. ESA is in charge of the space component, responsible for developing the family of Copernicus Sentinel satellites on behalf of the European Union and ensuring the flow of data for the Copernicus services, while the operations of the Copernicus Sentinels have been entrusted to ESA and EUMETSAT.
Did you know that?
Earth observation data from the Copernicus Sentinel satellites are fed into the Copernicus Services. First launched in 2012 with the Land Monitoring and Emergency Management services, these services provide free and open support, in six different thematic areas.
The Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) provides continuous data and information on atmospheric composition. It supports many applications in a variety of domains including health, environmental monitoring, renewable energies, meteorology and climatology.
References
[1] T. Lauvaux, et al., 2022, Global assessment of oil and gas methane ultra-emitters, Science, 375, 6580, 557-561, DOI: 10.1126/science.abj4351
[2] F. Vogel, 2022, Chasing after methane’s ultra-emitters, Science, 375, 6580, 490-491, DOI: 10.1126/science.abm1676
[3] European Commission, Communication From The Commission To The European Parliament, The Council, The European Economic And Social Committee And The Committee Of The Regions On An EU Strategy To Reduce Methane Emissions, Brussels, 14.10.2020 COM (2020) 663 final