Over the past summers, the Alta Murgia National Park in Southern Italy faced a lack of information on wildfires for post-fire assessments-Copernicus Sentinel-2 data came into action, enabling the design and development of Rheticus® Wildfires by Planetek Italia: a geo-information service offering solutions.
Wildfires represent a significant threat to environmental resources, with hundreds of thousands of hectares of burnt areas and invaluable loss of woods and biodiversity every year, in Italy and worldwide. Hot summer conditions raise the frequency, extent and severity of fires through increased temperatures and drought.
Climate change increments the risk of wildfires, allowing them to spark more easily and burn more. Together with climate change, negligence or setting fires, whether on purpose or not, can also influence wildfire patterns.
To correctly manage post-fire recovery activities, establishing a database of burn scars and keeping it up-to-date are crucial tasks. According to Italian laws, the Carabinieri Forestry Corps is in charge of forest-fire investigations and crime repression, including field surveys and mapping of burnt areas throughout the country.
On the other hand, municipalities are in charge of keeping burnt area databases up-to-date. But such activities are both costly and time-consuming. Furthermore, it is difficult to perform accurate field surveys over inaccessible areas. As a result, stakeholders that need such information, such as National and Regional Park Services, quite often face a lack of actionable information for keeping their fire prevention plans up-to-date, as required by the Italian laws, and for post-fire management and recovery planning.
Over the past years, the European Union's Copernicus Programme contributed to starting a new era of Big Data in the field of Earth Observation (EO), through the launch of the Sentinel satellites, which offer free and open data.
Thus, relevant satellite data are now freely available with high temporal and spatial resolutions. Benefits of using EO satellites are significant, especially for post-fire assessments, as this enables automatic and continual monitoring, regardless of the extent and morphology of the area of interest.
Furthermore, EO together with Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms and high computational capabilities, boost the possibility to address end-users' needs.
The Alta Murgia National Park in Southern Italy is one of Italy's 25 Parks. Created in 2004, it covers an area of about 68,000 ha. In 2017, to oversee and report fire activities, support fire management and recovery planning, the Park needed a solution that would continuously collect, visualise, and analyse burnt areas affecting its territory.
Planetek Italia was commissioned to assist the Alta Murgia National Park with monitoring and understanding areas affected by wildfires and Rheticus® Wildfires provided the park with a solution.
Rheticus® Wildfires by Planetek Italia is a high-performing and cloud-based geo-information service for post-fire monitoring. It provides end-users with essential information retrieved from Sentinel-2 satellites of the European Union's Copernicus Programme, together with other open data sources, through extensively tested models and algorithms.
The Park activated the service in July 2017—the first ones in Italy to adopt such an innovative service. Owing to the high revisit time of Copernicus Sentinel-2 over the same area (up to 5-6 days), and the high spectral and spatial resolutions of the data, Rheticus® Wildfires provided the Alta Murgia National Park with burnt area detection and fire severity classification every week. In addition, they provided vegetation regrowth monitoring (1/year) and detection of potential illegal infrastructure activities on previous-burnt areas (4 times/year).
Using Copernicus Sentinel-2 to continuously monitor wildfires
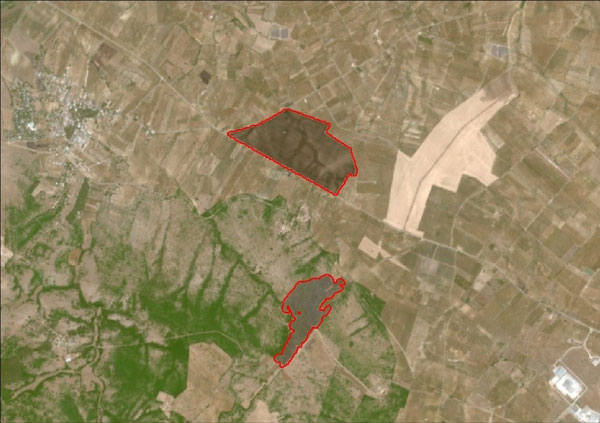
To assist with monitoring areas affected by wildfires, Rheticus® Wildfires continually tracks burnt areas via multispectral satellite data. Copernicus Sentinel-2 data are ideal for the task because they are readily available, frequently updated, and allow users to gain an insight with high accuracy.
Every time new Copernicus Sentinel-2 data are available over the end user's area of interest, the Rheticus® platform automatically downloads the image. It processes the latter downloaded image together with the former one, to detect new burn scars that occurred over the area of interest.
Then, on the Rheticus® cloud-based infrastructure, a dedicated database is updated with new events. The platform provides end-users with essential information retrieved from Copernicus Sentinel-2 together with other open data sources through extensively tested models and AI algorithms, to better classify burnt areas and reduced misclassified pixels.
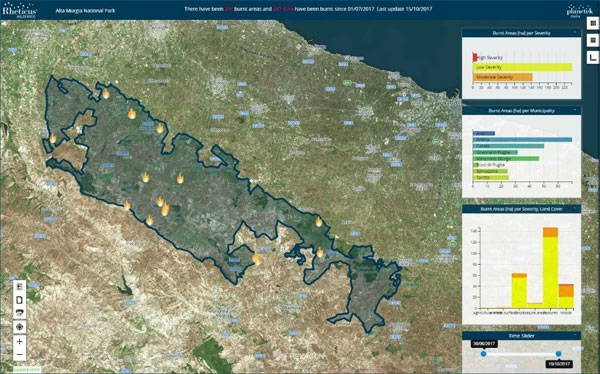
These insightful and purpose-built contents from many different perspectives are made available through a web-based application with thematic maps, geo-analytics and pre-set reports.
The Park's users obtained a synoptic point-of-view of the territory, with constant updates highlighting areas with slightly damaged areas versus those affected by severe damage to the vegetation. The service worked as a complementary diagnostic tool to in-situ monitoring activities.
For each burn scar, the service was able to collect and provide detailed levels of information, giving end-users the ability to analyse wildfires over time, with high precision and accuracy.
The complete picture provided by Rheticus® Wildfires gave the Park users the vital knowledge they needed to prioritise mitigation measures, make better decisions, and proactively avoid critical issues, which could have arisen, if in-progress phenomena had not been fully understood.
Data were available via the Rheticus® geo-portal and through pre-set reports.
Antonello Aiello, Technical Specialist of Rheticus in Planetek Italia, affirms, "It's crucial for National and Regional Park Services, decision-makers and stakeholders to have effective systems for collecting, visualising and monitoring burnt areas. With Rheticus®Wildfires, users get an accurate, comprehensive overview of their areas of interest, with timely updates and dynamics analytics.
"Because Rheticus® Wildfires uses readily available, open source Copernicus Sentinel-2 data, the Alta Murgia National Park has been able to reduce the time and efforts of their everyday duties significantly."
Aiello concludes that, "Copernicus Sentinels ensure continuity of service. This case history is expected to serve as a good example for the further promotion of the service at a European and global scale. The integration of Copernicus Sentinel-3 data is explored for further improvements to the processing chain".
Rheticus® beyond Wildfires
The Sentinel missions of the Copernicus Programme provide an unprecedented opportunity for operational Earth monitoring and service providers like Planetek Italia. Features such as data availability over a long time and worldwide, with scheduled revisit time, low-cost and high-quality data, are fundamental characteristics to build services that meet end-users' needs in a global market.
Moreover, the increasing volume and varieties of remote sensing data have generated new significant challenges in handling datasets, which require a new paradigm to extract relevant knowledge and actionable information for effective and efficient EO activities.
In light of the new Big Data era, it is not feasible for operators carry out the collection, management, processing and analysis of such a massive amount of data, using out-dated approaches. Thus, it is necessary to provide the EO community with automatic high-performing processes.
In the above mentioned steady-evolving scenario, information cannot be provided through traditional maps, but needs to be released in smart and more dynamic ways, through geo-analytics and Business Intelligence interfaces. Moreover, the adoption of cloud-based computing environments permits faster prototyping and more straightforward implementation of solutions than ever before.
Following this new philosophy, Planetek Italia designed and developed the cloud-based platform for automatic and continuous processing of satellite data, called Rheticus®, from the name of Nicolaus Copernicus' sole pupil. The platform consumes satellite data such as Sentinel images, weather data and other open data sources, to provide several continuous Earth monitoring services available under subscription, ranging from the detection and monitoring of geo-hazards and infrastructure instability, to marine water quality monitoring, from supporting aquaculture activities to wildfire detection, as well as land cover monitoring.
Among the innovations introduced by Rheticus®, shifting from a model of monitoring services on request to long-time information services subscriptions (IaaS) is the real disruptive innovation. End-users pay for the information, not for the processing, intended as continual access to actionable information.
European Services on wildfires
Since 1998, the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS) supports the services in charge of the protection of forests against fires in the EU and provides the European Commission services and the European Parliament with updated and reliable information on wildland fires in Europe.
Today it comprises the most up-to-date information on the current fire season in Europe and in the Mediterranean area, including meteorological fire danger maps and up to 6 day forecasts, daily updated maps of hot spots and fire perimeters.
About the Copernicus Sentinels
The Copernicus Sentinels are a fleet of dedicated EU-owned satellites, designed to deliver the wealth of data and imagery that are central to the European Union's Copernicus environmental programme.
The European Commission leads and coordinates this programme, to improve the management of the environment, safeguarding lives every day. ESA is in charge of the space component, responsible for developing the family of Copernicus Sentinel satellites on behalf of the European Union and ensuring the flow of data for the Copernicus services, while the operations of the Copernicus Sentinels have been entrusted to ESA and EUMETSAT.