In October 2017, a series of wildfires broke out in northern California, killing many and burning thousands of acres of land. Satellite imagery and particular data processing techniques are being used to help map the extent of the damage.
In October 2017, a series of wildfires broke out in northern California, killing many and burning thousands of acres of land. Satellite imagery and particular data processing techniques are being used to help map the extent of the damage.
Offering systematic observations over the globe, satellites are particularly useful when trying to assess and map the kind of widespread damage suffered by northern California recently.
Carrying a high-resolution multispectral instrument, the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission is used to monitor the health of Earth's vegetation and to map changes in land cover. However, by comparing satellite images acquired before and after events such as wildfires, Sentinel-2 can yield detailed data about the damage caused.
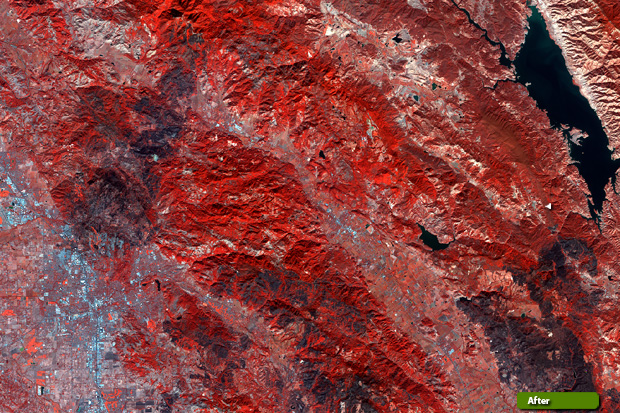
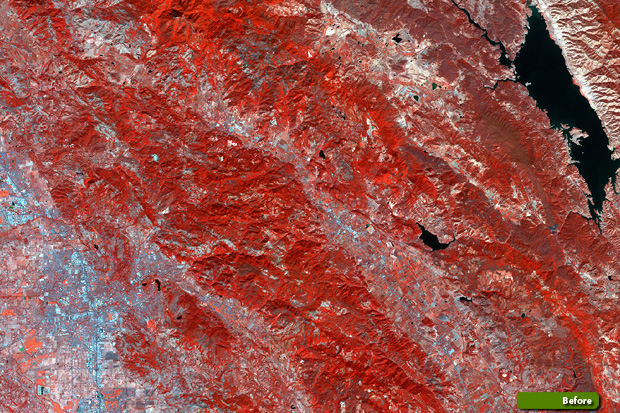


Since the two Sentinel-2 satellites image the surface of Earth with a 290 km-wide swath, most of our planet can be covered every five days. This means that it is an ideal mission to use for generating background reference maps that are not only consistent, but that can also be updated frequently.
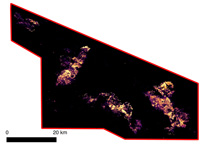
The Normalised burn ratio (NBR) is a formula that can be applied to the mission's multispectral data, which highlights areas that have been burnt, and can be used to estimate the severity of a fire.
Similar to a normalised difference vegetation index (NDVI), used in the past to identify burned areas, the NBR uses the near-infrared (NIR) and shortwave-infrared (SWIR) portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The NBR and differenced normalised burn ratio (dNBR) were specifically developed to estimate fire severity.
Descartes Labs, a data refinery company, has created a cloud-based supercomputing platform to apply machine intelligence to massive datasets. They combine data from multiple sources with the aim of generating, validating, and disseminating datasets to emergency response units and government agencies to address the impact of natural disasters.
Using land-cover maps classified by the US Department of Agriculture and maps created using data from the US Landsat mission and Sentinel-2, they were able to get a better understanding of the different types of vegetation that had been most affected by the wildfires in northern California.
This method was used to show intense burning throughout much of the region on 12 October.
"By comparing the areas affected by the wildfires with land-cover data from the USDA, we get a better understanding of where the most severe damage occurred," says Caitlin Kontgis, a Geographer at Descartes Labs.
"Also, we can gain these insights while the fire is still active. Our analysis is from 12 October, when the fire was still burning and we found that 45,000 of 96,000 acres were severely burned. Shrub land made up 50% of the damaged area. We need ground-truth data to confirm these percentages, but we are certain that this type of mapping is a giant step in helping understand where to focus recovery efforts, ranging from ecosystem restoration to rebuilding."
Ferran Gascon, ESA's Sentinel-2 Mission Manager, adds, "The Sentinel-2 satellites are exceptional for capturing the full extent of burn scars as well as identifying the types of vegetation that have been affected by wildfires. By combining Sentinel-2 with other sensors, maps can be updated regularly, timely and be readily distributed to those who need them most."
About the Sentinels
The Sentinels are a fleet of dedicated EU-owned satellites, designed to deliver the wealth of data and imagery that are central to Europe's Copernicus environmental programme.
In partnership with EU Member States, the European Commission leads and coordinates this programme, to improve the management of the environment, safeguarding lives every day. ESA is in charge of the space component, responsible for developing the family of Copernicus Sentinel satellites and ensuring the flow of data for the Copernicus services, while the operations of the Sentinels have been entrusted to ESA and EUMETSAT.